Mining
Wednesday, July 20th, 2022 12:26 pm EDT
The peer reviewed paper, “The overlooked mechanism of chalcopyrite passivation” was published in Acta Materialia, and sheds new light on how chalcopyrite behaves when subject to leaching and provides a better understanding of the nature of the passivation layer, which has been the topic of debate and dispute for several decades. The passivation layer forms on the surface of chalcopyrite and other primary sulfide minerals, preventing leaching from occurring effectively.
Related: Jetti Resources’ quest for copper mining’s holy grail
In the study, the team used electrochemical analysis to discover that chalcopyrite is an n-type semiconductor in an accumulation state, not in a depletion state as has been commonly assumed to date.
Jetti’s researchers demonstrated how during oxidative leaching, such as bioleach or chloride leach processes, a copper rich surface forms on the surface of the chalcopyrite. This rich product layer is a p-type semiconductor.
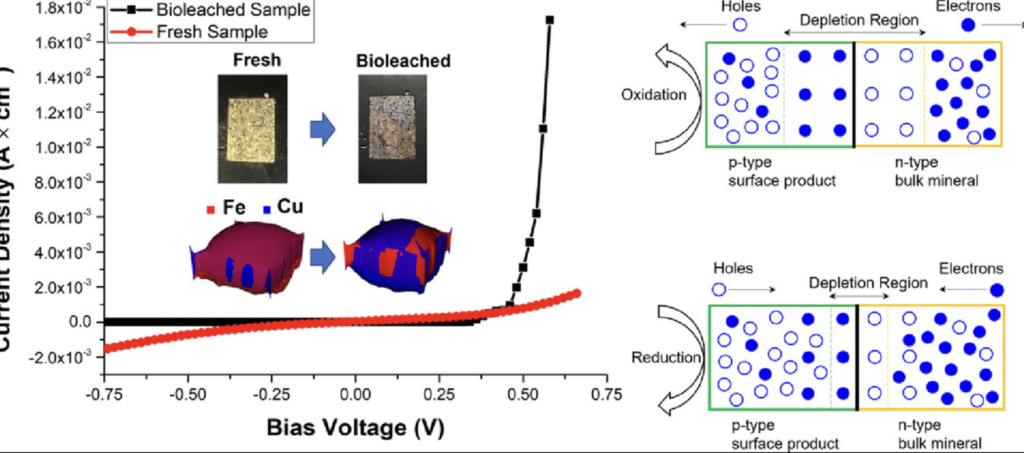
Analysis of the data allowed the scientists to discover that, as leaching progresses, the n-type semiconductor chalcopyrite surface and the p-type semiconductor of the product layer form a p-n junction diode which hinders the electrochemical leaching process as it blocks the transfer of electrons.
“This research clearly illustrates the unrivalled technical understanding that Jetti and UBC have built in copper leaching,” Jetti CEO Mike Outwin said in the statement. “Jetti’s catalytic technology has been commercially producing copper for years, and this unique insight will enable us to further enhance our technological leadership to meet growing demand for copper from the energy transition.”
“Working in partnership with the Jetti team, we have solved the issue that has long been described as the “holy grail” of the copper industry,” UBC Professors David Dixon and Edouard Asselin.
“Our research enables a much fuller understanding of the process involved in copper leaching.”
Read the full paper here.
This post has been syndicated from a third-party source. View the original article here.




